Following are difference between linear guides and rotary bearings.
1. Function and mode of exercise
Linear guides
Function: It is mainly used to achieve linear motion to guide equipment or components to make precise linear movement in a specific direction.
Mode of motion: The carrying object reciprocates in a straight line along a fixed track, and the trajectory is a straight line. In automated production lines, for example, material handling devices move smoothly in the horizontal direction via linear guides, transporting products from one station to another.
Rotating bearings
Function: Supports rotational motion, reduces friction and wear between rotating parts, and enables the shaft to rotate smoothly around its axis.
Mode of movement: Rotational motion around a central point. For example, the rotating shaft in the motor is supported by a rotating bearing, which rotates at high speed to drive other components to work.
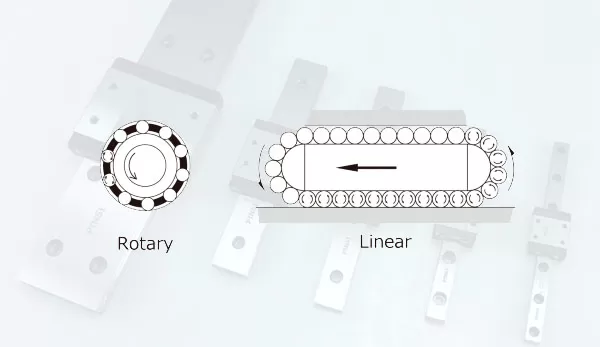
2. Structural characteristics
Linear guides
It usually consists of a guide rail and a slider. The guide rail is a part of the track fixed on the foundation of the equipment, which has a specific shape and precision requirements, and is generally in the form of a long strip. The slide is mounted on the part to be moved, and contains balls, rollers or sliding materials, etc., which work with the guide rail to achieve smooth linear movement.
The shape is relatively regular, the size is relatively large, and the length can be customized according to actual needs.
Rotating bearings
It is mainly composed of an inner ring, an outer ring, rolling elements (such as balls, rollers) and a cage. The inner and outer rings are connected to the axis of rotation and the fixed parts, respectively, the rolling elements roll between the two, and the cage is used to separate and guide the rolling elements.
The structure is relatively compact, usually ring-shaped, and is available in different diameters and widths.
3. Application scenarios
Linear guides
It is suitable for occasions that require precise linear motion, such as CNC machine tools, laser cutting equipment, printing machinery, etc. In these machines, linear guides ensure machining accuracy and stability of movement.
In the automated warehousing system, the stacker crane moves accurately between the shelves through linear guide rails to realize the storage and retrieval of goods.
Rotating bearings
It is widely used in various rotating machinery, such as automobile wheels, motors, fans, pumps, etc. In these devices, rotating bearings support rotating parts, reduce friction and transmit power.
Rotating bearings are installed in the wheels of bicycles, which allow the wheels to rotate smoothly and reduce resistance when riding.
4. Accuracy requirements
Linear guides
It has high requirements for accuracy indicators such as straightness, parallelism, and perpendicularity. The high-precision linear guide rail can achieve micron-level or even higher linear motion accuracy to ensure the accuracy of the equipment in the process of processing and measurement.
For example, in the adjustment device of precision optical instruments, the accuracy of the linear guide directly affects the adjustment accuracy and performance of the instrument.
Rotating bearings
It mainly focuses on rotation accuracy, radial runout, axial runout and other indicators. High-precision rotating bearings ensure smooth operation of the rotating shaft and reduce vibration and noise.
In high-speed motors, the precision requirements of the rotating bearings are very high to ensure the stability and reliability of the motor at high speeds.
5. Carrying capacity
Linear guides
It usually has a large load-bearing capacity and can withstand pressure perpendicular to the direction of the guide rail and a certain lateral force. The magnitude of the load-bearing capacity depends on the size, material and structural design of the rails.
In heavy machinery and equipment, it is necessary to select linear guide rails with strong bearing capacity to ensure the stability and safety of the equipment during operation.
Rotating bearings
It mainly bears radial and axial loads. Different types of rotating bearings have different load carrying capacity, and it is generally necessary to select the appropriate bearing model and specification to meet the load bearing requirements of the equipment.
For example, in the lifting mechanism of cranes, large rotating bearings need to be subjected to huge radial and axial loads.


 +8615622924499
+8615622924499
 +8615622924499
+8615622924499

