Understanding the Linear Guide Block:
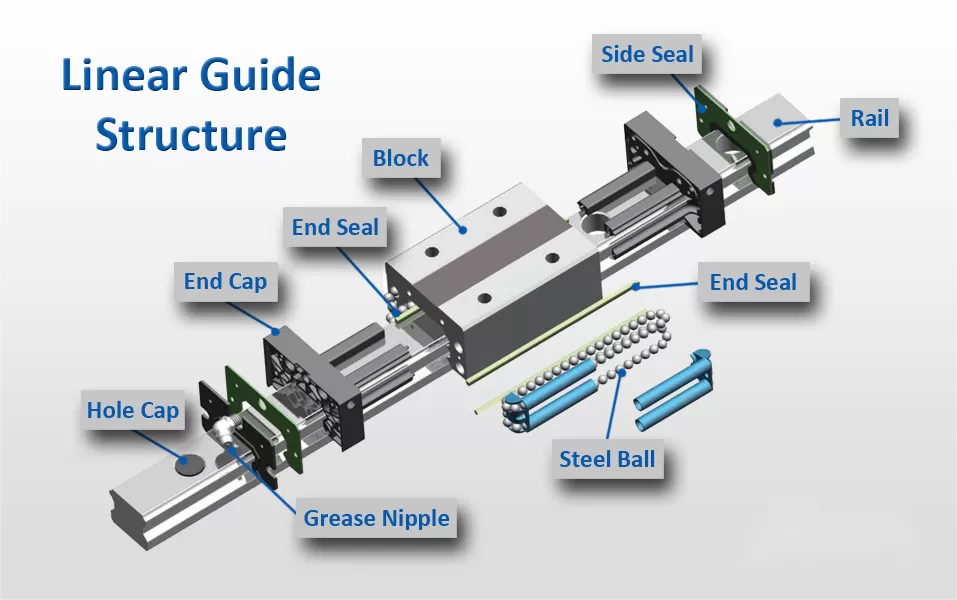
A linear guide block, often referred to as a carriage or slider, is a key component of a linear motion system. Its primary function is to facilitate the controlled and precise movement of loads along a linear guide rail. This component is typically mounted on the rail, allowing it to move in a straight line, and it plays a crucial role in supporting, guiding, and carrying the applied load.
Components of a Linear Guide Block:
A typical linear guide block consists of several components, each contributing to its functionality:
1. Body: The body of the guide block is the main structure that interfaces with the linear guide rail. It provides stability and rigidity to the entire assembly.
2. Rolling Elements: Most linear guide blocks utilize rolling elements, such as ball bearings or rollers, to reduce friction and facilitate smooth motion along the guide rail. The rolling elements are typically arranged in a circular pattern within the body.
3. Load Carrying Elements: These components are responsible for bearing the load applied to the linear guide block. They ensure that the weight or force is evenly distributed, preventing excessive wear and ensuring consistent movement.
4. Seals and Lubrication:
- Seals: Seals or wipers are often integrated into the linear guide block to protect the rolling elements from contamination and debris, ensuring reliable operation.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction, minimize wear, and maintain efficient motion. Lubrication channels or reservoirs may be built into the linear guide block.
Applications of Linear Guide Blocks:
Linear guide blocks find applications in a wide range of industries and machinery, including:
1. Machine Tools: Linear guide blocks are essential in CNC machines, milling machines, and lathes, where precise and rigid linear motion is crucial for machining operations.
2. Automation and Robotics: They are widely used in robotic arms and automated assembly lines, enabling controlled and repeatable motion.

3. Medical Equipment: Linear guide blocks are found in medical imaging equipment, surgical robots, and precision positioning systems.
4. Packaging and Material Handling: They play a role in packaging machinery and conveyor systems, ensuring efficient and reliable product handling.
Choosing the Right Linear Guide Block:
Selecting the appropriate linear guide block depends on various factors, including load capacity, precision requirements, environmental conditions, and space constraints. PINSI offers a diverse range of linear guide blocks designed to meet the specific needs of different applications, providing a reliable solution for your linear motion requirements.
Conclusion:
The linear guide block is a fundamental component in linear motion systems, serving as the workhorse that enables precise and controlled linear movement in various applications. Understanding its role and the components that comprise it is crucial for selecting the right solution for your specific industrial needs. PINSI's commitment to quality ensures that our linear guide blocks are designed to deliver the reliability and performance demanded by a diverse range of industries.


 +8615622924499
+8615622924499
 +8615622924499
+8615622924499

